Five pillars of Atmanirbhar Bharat – Economy, Infrastructure, System , Vibrant Demography and Demand.
Special economic and comprehensive package of Rs 20 lakh crores – equivalent to 10% of India’s GDP.
Download Link for Details of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan- Part 1
Next part of article deals ONLY with those Topics and Explanation of Terms from the above PDF file which are important for Prelims Exam 2020 .
( One does not need to memorize whole PDF File,only relevant points,but one must go through the whole document properly)
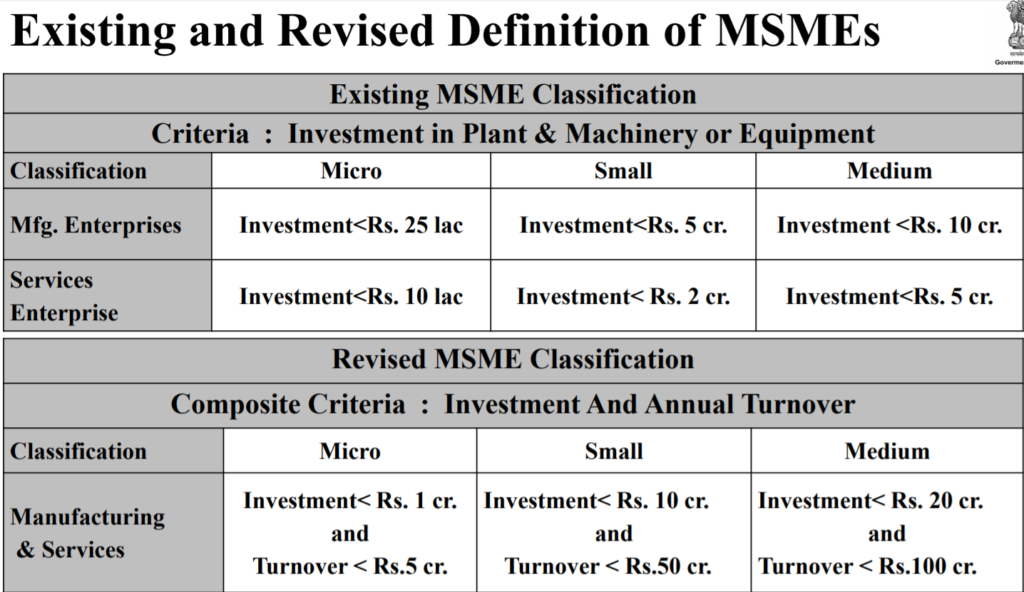
(Accessible only to Pro-subscribers)
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package
Features
- Insurance cover of Rs 50 Lakh per health worker
- 80 crore poor people given benefit of 5 kg wheat or rice per person for next 3 months
- 1 kg pulses for each household for free every month for the next 3 months
- 20 crore women Jan Dhan account holders get Rs 500 per month for next 3 months
- Gas cylinders, free of cost, provided to 8 crore poor families for the next 3 months
- Increase in MNREGA wage to Rs 202 a day from Rs 182 to benefit 13.62 crore families
- Ex-gratia of Rs 1,000 to 3 crore poor senior citizen, poor widows and poor Divyang.
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package (2)
- Front-loaded Rs 2,000 paid to farmers under existing PM-KISAN to benefit 8.7 crore farmers
- Building and Construction Workers Welfare Fund allowed to be used to provide relief to workers
- 24% of monthly wages to be credited into their PF accounts for next three months for wage-earners below Rs 15,000 p.m. in businesses having less than 100 workers
- Five crore workers registered under Employee Provident Fund EPF to get non-refundable advance of 75% of the amount or three months of the wages, whichever is lower, from their accounts
- Limit of collateral free lending to be increased from Rs 10 to Rs 20 lakhs for Women Self Help Groups supporting 6.85 crore households.
- District Mineral Fund (DMF) to be used for supplementing and augmenting facilities of medical testing, screening etc..
PM-KISAN Scheme
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is a Central Sector scheme with 100% funding from Government of India.
- Under the Scheme an income support of Rs.6000/- per year is provided to all farmer families across the country in three equal installments of Rs.2000/- each every four months.
- Definition of family for the Scheme is husband, wife and minor children.
- The entire responsibility of identification of beneficiary farmer families rests with the State / UT Governments.
- The fund is directly transferred to the bank accounts of the beneficiaries.
District Mineral Foundation,MMDRA 2015
- District Mineral Foundation (DMF) is a trust set up as a non-profit body, in those districts affected by the mining works, to work for the interest and benefit of persons and areas affected by mining related operations. It is funded through the contributions from miners.
- Under jurisdiction of State governments.
- Mandated through the Mines and Minerals (Development & Regulation) Amendment Act, (MMDRA) 2015.
- Central Government retains the power to prescribe the rates of contribution.
- The contributions made to DMFs are collected by the State Governments .
- Under the above mentioned MMRD Amendment Act of 2015, a provision was made also to create a National Mineral Exploration Trust under the jurisdiction of central government, with 2% of royalty as levy, for boosting detailed exploration of minerals.
- DMF funds are treated as extra-budgetary resources for the State Plan.
- Composition and functions of the DMF are prescribed by the State Government.
- DMFs are expected to implement the Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY), launched on 17 September 2015 for the welfare of mining areas and affected population.
Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY):
- This programme meant to provide for the welfare of areas and people affected by mining related operations. The most productive mining areas in the country are largely areas inhabited by scheduled tribes. They also are mainly located in the areas covered by the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution. The PMKKKY is, therefore, very sharply focused on safeguarding the health, environment and economic conditions of the tribals and providing them with opportunities to benefit from the vast mineral resources that are extracted from the areas where they live.
Ways and Means Advances
It is a facility for both the Centre and states to borrow from the RBI. These borrowings are meant purely to help them to tide over temporary mismatches in cash flows of their receipts and expenditures. In that sense, they aren’t a source of finance per se. Section 17(5) of the RBI Act, 1934 authorises the central bank to lend to the Centre and state governments subject to their being repayable “not later than three months from the date of the making of the advance”.
The interest rate on WMA is the RBI’s repo rate, which is basically the rate at which it lends short-term money to banks.
Cash Reserve Ratio
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is a specified minimum fraction of the total deposits of customers, which commercial banks have to hold as reserves either in cash or as deposits with the central bank. CRR is set according to the guidelines of the central bank of a country.
- The aim here is to ensure that banks do not run out of cash to meet the payment demands of their depositors.
- CRR is a crucial monetary policy tool and is used for controlling money supply in an economy.
- CRR specifications give greater control to the central bank over money supply.
- Commercial banks have to hold only some specified part of the total deposits as reserves. This is called fractional reserve banking.
Long Term Repo Operation(LTRO)
In the last monetary policy, instead of cutting the policy rates, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced a tool called long-term repo operation (LTRO) to inject liquidity in the system, as well as to ensure transmission of rates.
Under LTRO, RBI provides longer term (one- to three-year) loans to banks at the prevailing repo rate. As banks get long-term funds at lower rates, their cost of funds falls. In turn, they reduce interest rates for borrowers. LTRO helped RBI ensure that banks reduce their marginal cost of funds-based lending rate, without reducing policy rates.
Marginal Standing Facility
Definition: Marginal standing facility (MSF) is a window for banks to borrow from the Reserve Bank of India in an emergency situation when inter-bank liquidity dries up completely.
Description: Banks borrow from the central bank by pledging government securities at a rate higher than the repo rate under liquidity adjustment facility or LAF in short. The MSF rate is pegged 100 basis points or a percentage point above the repo rate. Under MSF, banks can borrow funds up to one percentage of their net demand and time liabilities (NDTL).
Non Banking Finance Company – NBFC
A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 engaged in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds/debentures/securities issued by Government or local authority or other marketable securities of a like nature, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance business, chit business but does not include any institution whose principal business is that of agriculture activity, industrial activity, purchase or sale of any goods (other than securities) or providing any services and sale/purchase/construction of immovable property.
What is difference between banks & NBFCs?
NBFCs lend and make investments and hence their activities are akin to that of banks; however there are a few differences as given below:
- NBFC cannot accept demand deposits;
- NBFCs do not form part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue cheques drawn on itself;
- deposit insurance facility of Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation is not available to depositors of NBFCs, unlike in case of banks.
NABARAD
- Apex banking institution to provide finance for Agriculture and rural development.
- It is a statutory body established in 1982 under Parliamentary act-National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development Act, 1981.
- Established on July 12, 1982 with the paid up capital of Rs. 100 cr. by 50: 50 contribution of government of India and Reserve bank of India.
- Rural credit structure for providing credit for promotion of agriculture, small scale industries, cottage and village industries, handicrafts etc.
- It supervises Cooperative Banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) and helping them develop sound banking practices and integrate them to the CBS (Core Banking Solution) platform.
- It provides training to handicraft artisans and helps them in developing a marketing platform for selling these articles.
- NABARD provides recommendations to Reserve Bank of India on issue of licenses to Cooperative Banks, opening of new branches by State Cooperative Banks and Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
- NABARD had launched the Self Help Group-Bank Linkage Programme (SHG-BLP) in 1992.
- EShakti: In a bid to digitise SHGs, project EShakti was launched on 15 March 2015.
Small Industries Development Bank of India- SIDBI
- Development financial institution in India, headquartered at Lucknow .
- Its purpose is to provide refinance facilities and short term lending to industries, and serves as the principal financial institution in the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector.
- Statutory Body established on 1990.
- SIDBI operates under the Department of Financial Services, Government of India.
- State Bank of India is the largest individual shareholder of SIDBI , followed by Government of India and Life Insurance Corporation of India.
National Housing Bank
- Statutory body set up in 1988.
- Apex financial institution for housing.
- Powers of regulation of housing finance companies to Reserve Bank of India.
- Registers and supervises Housing Finance Company (HFCs).
4 All India Financial Institutions regulated and supervised by the Reserve Bank-
- EXIM Bank
- NABARD
- NHB
- SIDBI