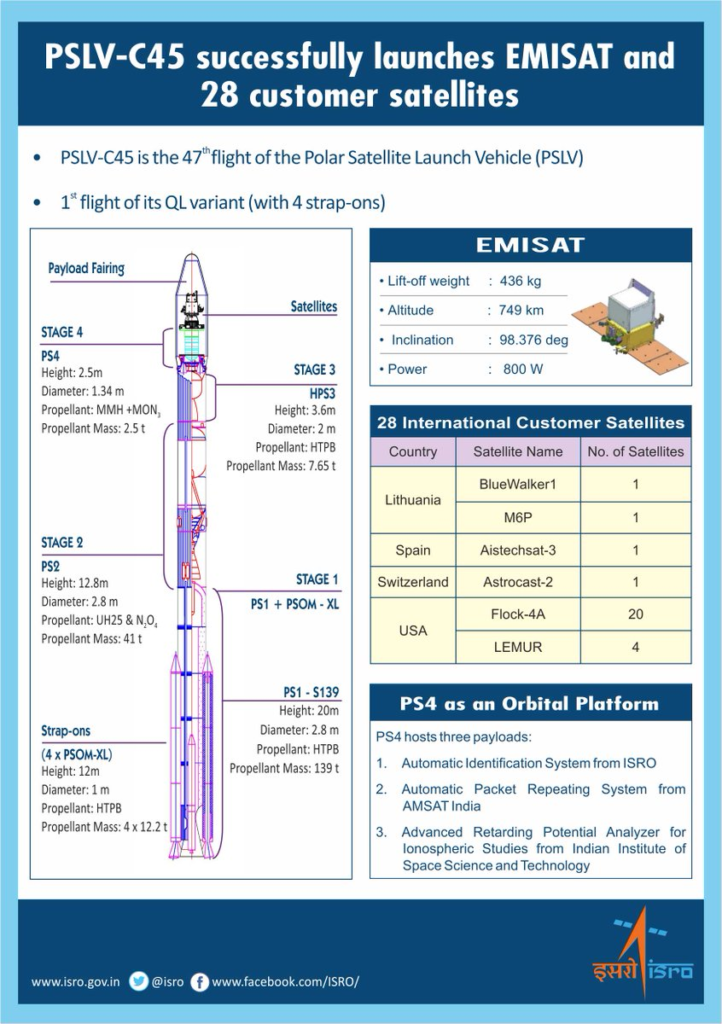
The PSLV-C45 / EMISAT MISSION
– 47th mission of the Indian Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) program
– launched on 1 April 2019 with a payload of 29 satellites, including one for electronic intelligence,along with 28 customer satellites from other countries.
– launched from the Second launch pad of the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra pradesh,India
– It carried primary payloads like EMISAT and secondary payloads like M6P, Bluewalker1, four Lemur-2 out of a total of thirty satellites.
– EMISAT is developed by DRDO.The EMISAT satellite is based on the IMS-2 bus inherited from SARAL.
– It was the first flight of PSLV-QL having 4 strap-on boosters and placed a primary payload EMISAT and a secondary payload of Lemur M6P in sun-synchronous orbits.
Uniqueness of the project
The specialty of this mission is that for the first time PSLV will launch satellites in Three different orbits.
Another distinguished feature of the project is for the first time, PSLV with four strap-on configuration has been identified for this mission.Till now, PSLV has been in either two or six strap-on configuration or without any strap-ons.
Third uniqueness in this mission as it is the first PSLV fourth stage (PS4) that uses solar panels to support payloads hosted on it.
Propellant:
Stage 1: Composite Solid
Stage 2: Earth Storable Liquid
Stage 3: Composite Solid
Stage 4: Earth Storable Liquid
Altitude: 780 kilometres (485 mi)
EMISAT MISSION
– India’s first electronic surveillance satellite, EMISAT.
– Space-based electronic intelligence or ELINT from the 436-kg spacecraft will add teeth to situational awareness of the Armed Forces as it will provide location and information of hostile radars placed at the borders; this will be another dimension to current land or aircraft-based ELINT.
– The spacecraft would measure the electromagnetic spectrum.
The ISRO Telemetry Tracking and Command Network at Bengaluru assumed control of the satellite.
Image provided by ISRO on PSLV-C45/EMISAT Mission -
PSLV – C44- Microsat – R and KalamSAT-V2
Jan 24, 2019-India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C44) successfully injected Microsat-R and Kalamsat-V2 satellites into their designated orbits.
Microsat – R
– 740-kg , an imaging satellite meant for military purposes
– Microsat-R is an small Indian satellite built for the Indian military Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO), likely as a target satellite for ASAT testing.
– orbits the earth at a height of 274 km.
Kalam SAT
– “World’s lightest and smallest satellite”
– Kalam SAT is a micro Satellite. It is named after former Indian president Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam.
– Kalamsat is a payload developed by students and Chennai based Space Kidz India for the first time.
– The probe is composed of 3-D printed reinforced carbon fiber polymer. The probe was launched by a sub-orbital spaceflight.
– The tiny probe will be operated only for less than 12 minutes to demonstrate the performance of 3-D printed carbon fiber in a micro-gravity environment of space.
– The Kalamsat is the first to use the rocket`s fourth stage as an orbital platform .
PSLV-C43 / HysIS Mission
PSLV-C43 lifted off at 0957 hrs (IST) on November 29, 2018 from the First Launch Pad (FLP) of Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota and successfully launched India’s Hyper spectral Imaging Satellite (HysIS) and 30 international co-passenger satellites.
HysIS Mission
The primary satellite of PSLV-C43 mission, weighing about 380 kg, is an earth observation satellite configured around ISRO’s Mini Satellite-2 (IMS-2) bus.
The primary goal of HysIS is to study the earth’s surface in the visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
PSLV-C42 Mission/NovaSAR & S1-4
PSLV-C42 Successfully Launched two foreign satellites from Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), SHAR, Sriharikota on September 16, 2018.
This mission was designed to launch two earth observation satellites, NovaSAR and S1-4 (together weighing nearly 889 kg) of M/s Surrey Satellite Technologies Limited (SSTL), United Kingdom under commercial arrangement with Antrix Corporation Limited, Department of Space. Both satellites were injected into 583 km Sun Synchronous Orbit.
NovaSAR is a S-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar satellite intended for forest mapping, land use & ice cover monitoring, flood & disaster monitoring.
S1-4 is a high resolution Optical Earth Observation Satellite, used for surveying resources, environment monitoring, urban management and for the disaster monitoring.
PSLV-C41/IRNSS-1I
April 12-2018
India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, in its forty-third flight (PSLV-C41) in XL configuration launched IRNSS-1I Satellite from First Launch Pad (FLP) of SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota. The ‘XL’ configuration of PSLV is used for the twentieth time.
The IRNSS-1I is the eighth satellite to join the NavIC navigation satellite constellation.
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) : NavIC
IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system being developed by India. It is designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1500 km from its boundary, which is its primary service area.
IRNSS will provide two types of services, namely,
- Standard Positioning Service (SPS) which is provided to all the users and
- Restricted Service (RS), which is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users (asked in UPSC – 2015-16).
The IRNSS System is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
Some applications of IRNSS are – (asked in Prelims 2014-15)
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation
- Disaster Management
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management
- Integration with mobile phones
- Precise Timing
- Mapping and Geodetic data capture
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travellers
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers
Also read about Mission Shakti from the link given below-
