A Multilateral Export Control Regime is an international body that states use to organize their national export control systems.
There are currently four such regimes:
1.The Wassenaar Arrangement (WA) on Export Controls for Conventional Arms and Dual-Use Goods and Technologies
2.The Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG), for the control of nuclear related technology
3.The Australia Group (AG) for control of chemical and biological technology that could be weaponized
4.The Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) for the control of rockets and other aerial vehicles capable of delivering weapons of mass destruction.
1.WASSENAAR ARRANGEMENT
(Not to be confused with the Wassenaar Agreement)
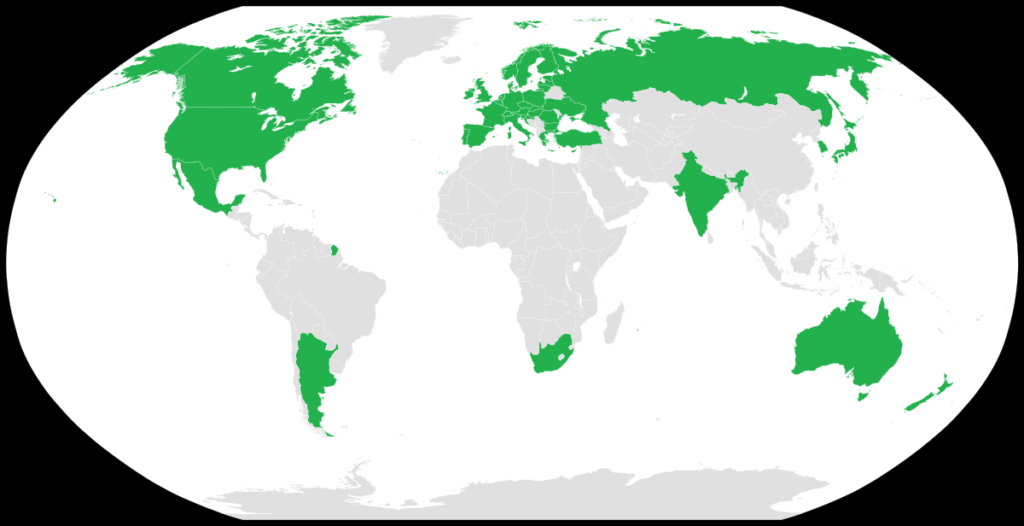
The Wassenaar Arrangement on Export Controls for Conventional Arms and Dual-Use Goods and Technologies is a multilateral export control regime (MECR) with 42 participating states .The Wassenaar Arrangement was established to contribute to regional and international security and stability by promoting transparency and greater responsibility in transfers of conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies.
– established on 12 July 1996, in Wassenaar, the Netherlands
-Secretariat- Vienna, Austria
Important Points-
1.India is the 42nd member since 2017.
2.China and Israel are not members.
3.Admission of new members requires the consensus of all members.
2.NUCLEAR SUPPLIERS GROUP

The Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) is a multilateral export control regime and a group of nuclear supplier countries that seek to prevent nuclear proliferation by controlling the export of materials, equipment and technology that can be used to manufacture nuclear weapons.
-“Non-Proliferation Principle” adopted in 1994, whereby a supplier, notwithstanding other provisions in the NSG Guidelines, authorises a transfer only when satisfied that the transfer would not contribute to the proliferation of nuclear weapons.
-The NSG was founded in response to the Indian nuclear test in May 1974 and first met in November 1975.
–48 members
-India is a not a member.China is a member.
3.Australia Group
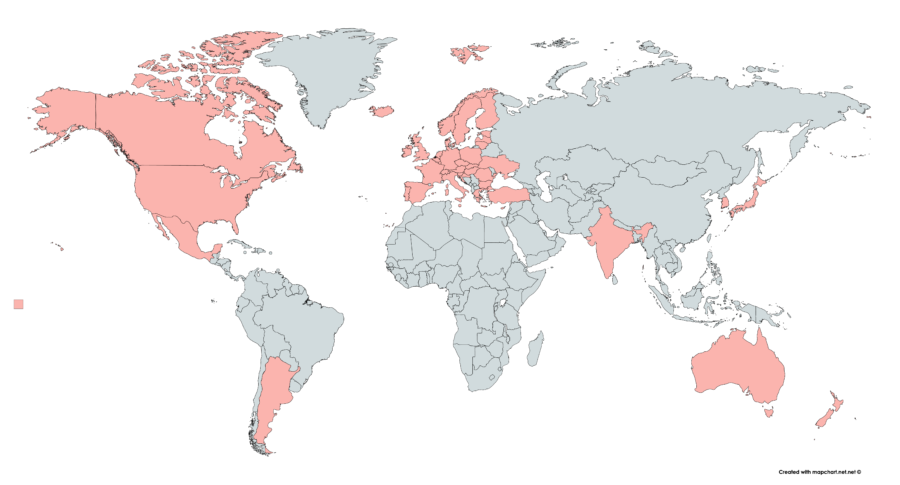
The Australia Group is a multilateral export control regime (MECR) and an informal group of countries (now joined by the European Commission) established in 1985 (after the use of chemical weapons by Iraq in 1984) to help member countries to identify those exports which need to be controlled so as not to contribute to the spread of chemical and biological weapons.
–“no-undercut” requirement – any member of the group considering making an export to another state that had already been denied an export by any other member of the group must first consult with that member state before approving the export.
–“catch-all” provision – member states to halt all exports that could be used by importers in chemical or biological weapons programs, regardless of whether the export is on the group’s control lists.
-Paris,France- venue of meeting every year
–India is the last member. China is not a member.
–43 members.
4.Missile Technology Control Regime
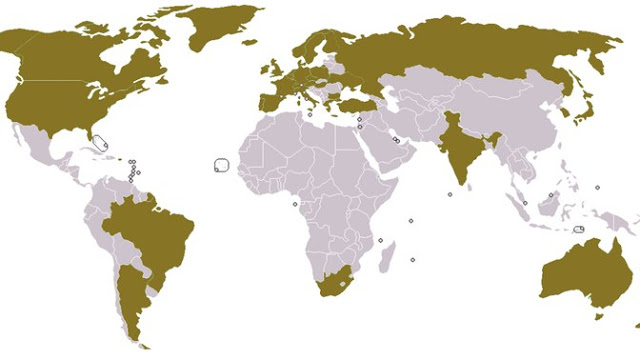
Established in April 1987, the voluntary Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) aims to limit the spread of ballistic missiles and other unmanned delivery systems that could be used for chemical, biological, and nuclear attacks. The regime urges its 35 members,which include most of the world’s key missile manufacturers, to restrict their exports of missiles and related technologies capable of carrying a 500-kilogram payload at least 300 kilometers or delivering any type of weapon of mass destruction
Important Points-
1.India is a member.
2.China is not a member.
3.MTCR is not a treaty and does not impose any legally binding obligations on Partners.
4.The regime was formed in 1987 by the G-7 industrialized countries
5.It is an informal political understanding among states.
6.Category I items include complete rocket and unmanned aerial vehicle systems (including ballistic missiles, space launch vehicles, sounding rockets, cruise missiles, target drones, and reconnaissance drones), capable of delivering a payload of at least 500 kg to a range of at least 300 km.Pursuant to the MTCR Guidelines, exports of Category I items are subject to an unconditional strong presumption of denial .
Category II items include other less-sensitive and dual-use missile related components, as well as other complete missile systems capable of a range of at least 300 km, regardless of payload. Their export is subject to licensing requirements taking into consideration the non-proliferation factors specified in the MTCR Guidelines.



